PhoenixMiner command line arguments
You can use this list as a reference for all Launch Parameters supported by PhoenixMiner.
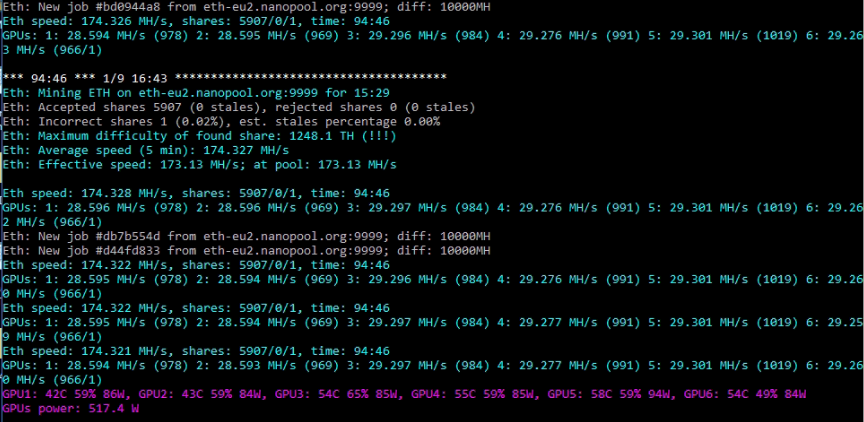
You can download PhoenixMiner 6.2c from here:
Linux:
Under Linux you need to replace PhoenixMiner.exe with ./PhoenixMiner in the command-line examples below.
Note that PhoenixMiner supports most of the command-line options of Claymore’s dual Ethereum miner so you can use the same command line options as the ones you would have used with Claymore’s miner.
Pool options
- -pool <host:port>
- Ethash pool address (prepend the host name with
ssl://for SSL pool, orhttp://for solo mining). - -wal <wallet>
- Ethash wallet (some pools require appending of user name and/or worker).
- -pass <password>
- Ethash password (most pools don’t require it, use
xas password if unsure). - -worker <name>
- Ethash worker name (most pools accept it as part of wallet).
- -proto <n>
- Selects the kind of stratum protocol for the ethash pool:
- 1
- miner-proxy stratum spec (e.g. coinotron)
- 2
- eth-proxy (e.g. ethermine, nanopool) - this is the default, works for most pools
- 3
- qtminer (e.g. ethermine, ethpool)
- 4
- EthereumStratum/1.0.0 (e.g. nicehash)
- 5
- EthereumStratum/2.0.0
- -coin <coin>
- Ethash coin to use for devfee to avoid switching DAGs:
- auto
- Auto-detect the coin (default)
- eth
- Ethereum
- etc
- Ethereum Classic
- exp
- Expanse
- music
- Musicoin
- ubq
- UBIQ
- pirl
- Pirl
- ella
- Ellaism
- etp
- Metaverse ETP
- whale
- WhaleCoin
- vic
- Victorium
- nuko
- Nekonium
- mix
- Mix
- egem
- EtherGem
- clo
- Callisto
- dbix
- DubaiCoin
- moac
- MOAC
- etho
- Ether-1
- yoc
- Yocoin
- b2g
- Bitcoiin2Gen
- esn
- Ethersocial
- ath
- Atheios
- reosc
- REOSC
- qkc
- QuarkChain
- bci
- Bitcoin Interest
- -stales <n>
- Submit stales to ethash pool: 1 - yes (default), 0 - no
- -pool2 <host:port>
- Failover ethash pool address. Same as
-poolbut for the failover pool - -wal2 <wallet>
- Failover ethash wallet (if missing
-walwill be used for the failover pool too) - -pass2 <password>
- Failover ethash password (if missing
-passwill be used for the failover pool too) - -worker2 <name>
- Failover ethash worker name (if missing
-workerwill be used for the failover pool too) - -proto2 <n>
- Failover ethash stratum protocol (if missing
-protowill be used for the failover pool too) - -coin2 <coin>
- Failover devfee Ethash coin (if missing
-coinwill be used for the failover pool too) - -stales2 <n>
- Submit stales to the failover pool: 1 - yes (default), 0 - no
- -dpool <host:port>
- Dual mining pool address
- -dwal <wallet>
- Dual mining wallet
- -dpass <password>
- Dual mining pool password (most pools don’t require it, use
xas password if unsure) - -dworker <name>
- Dual mining worker name
- -dcoin blake2s
- Currently only the Blake2s algorithm is supported for dual mining. If you want to put all dual mining pools in
dpools.txt, you need to set-dcoin blake2sin the command-line or in config.txt to force the miner to load the dual mining pools fromdpools.txt - -dstales <n>
- Submit stales to the dual mining pool: 1 - yes (default), 0 - no
General pool options
- -fret <n>
- Switch to next pool afer N failed connection attempts (default: 3)
- -ftimeout <n>
- Reconnect if no new ethash job is receved for n seconds (default: 600)
- -ptimeout <n>
- Switch back to primary pool after n minutes. This setting is 30 minutes by default; set to 0 to disable automatic switch back to primary pool.
- -retrydelay <n>
- Seconds to wait before reconnecting (default: 5)
- -gwtime <n>
- Recheck period for Solo/GetWork mining (default: 200 ms)
- -rate <n>
- Report hashrate to the pool: 1 - yes, 0 - no (1 is the default), 2 - (for solo mining only) use alternative name of the report method
eth_submitHashRateinstead ofeth_submitHashrate
Benchmark mode
- -bench [<n>],-benchmark [<n>]
- Benchmark mode, optionally specify DAG epoch. Use this to test your rig. If you specify only the
-benchoption, you will benchmark the ethash algorithm. If you want to bench the dual mining, use the options-bench <n> -dcoin blake2s. If you want to benchmark the ProgPOW BCI algorithm, use the options-bench <n> -coin bci
Remote control options
- -cdm <n>
- Selects the level of support of the CDM remote monitoring:
- 0
- disabled
- 1
- read-only - this is the default
- 2
- full (only use on secure connections)
- -cdmport <port>
- Set the CDM remote monitoring port (default is 3333). You can also specify <ip_addr:port> if you have a secure VPN connection and want to bind the CDM port to it
- -cdmpass <pass>
- Set the CDM remote monitoring password
- -cdmrs
- Reload the settings if
config.txtis edited/uploaded remotely. Note that most options require restart in order to change. Currently the following options can be changed without restarting:-mi,-gt,-sci,-clf,-nvf,-gpow, and most of the hardware control parameters (-tt,-fcm,-fanmin,-fanmax,-powlim,-tmax,-ttli,-cclock,-cvddc,-mclock,-mvddc,-ppf,-straps,-vmt1,-vmt2,-vmt3,-vmr).
Mining options
- -amd
- Use only AMD cards
- -acm
- Turn on AMD compute mode on the supported GPUs. This is equivalent of pressing
yin the miner console. - -nvidia
- Use only Nvidia cards
- -gpus <123 ..n>
- Use only the specified GPUs (if more than 10, separate the indexes with comma)
- -mi <n>
- Set the mining intensity (0 to 14; 12 is the default for new kernels). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -gt <n>
- Set the GPU tuning parameter (6 to 400). The default is 15. You can change the tuning parameter interactively with the
+and-keys in the miner’s console window. You may specify this option per-GPU. If you don’t specify-gtor you specify value 0, the miner will use auto-tuning to determine the best GT value. Note that when the GPU is dual-mining, it ignores the-gtvalues, and uses-sciinstead. - -sci <n>
- Set the dual mining intensity (1 to 1000). The default is 30. As you increase the value of
-sci, the secondary coin hashrate will increase but the price will be higher power consumption and/or lower ethash hashrate. You can change the this parameter interactively with the+and-keys in the miner’s console window. You may specify this option per-GPU. If you set-scito 0, the miner will use auto-tuning to determine the best value, while trying to maximize the ethash hashrate regardless of the secondary coin hashrate. - -clKernel <n>
- Type of OpenCL kernel: 0 - generic, 1 - optimized, 2 - alternative, 3 - turbo (1 is the default) You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -clgreen <n>
- Use the power-efficient (“green”) kernels (0: no, 1: yes; default: 0). You may specify this option per-GPU. Note that you have to run auto-tune again as the optimal GT values are completely different for the green kernels
- -clNew <n>
- Use new AMD kernels if supported (0: no, 1: yes; default: 1). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -clf <n>
- AMD kernel sync (0: never, 1: periodic; 2: always; default: 1). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -nvKernel <n>
- Type of Nvidia kernel: 0 auto (default), 1 old (v1), 2 newer (v2), 3 latest (v3). Note that v3 kernels are only supported on GTX10x0 GPUs. Also note that dual mining is supported only by v2 kernels. You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -nvdo <n>
- Enable Nvidia driver-specific optimizations (0 - no, the default; 1 - yes). Try
-nvdo 1if your are unstable. You may specify this option per-GPU. - -nvNew <n>
- Use new Nvidia kernels if supported (0: no, 1: yes; default: 1). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -nvf <n>
- Nvidia kernel sync (0: never, 1: periodic; 2: always; 3: forced; default: 1). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -mode <n>
- Mining mode (0: dual mining if dual pool(s) are specified; 1: ethash only even if dual pools are specified). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -gbase <n>
- Set the index of the first GPU (0 or 1, default: 1)
- -minRigSpeed <n>
- Restart the miner if avg 5 min speed is below <n> MH/s
- -eres <n>
- Allocate DAG buffers big enough for n epochs ahead (default: 2) to avoid allocating new buffers on each DAG epoch switch, which should improve DAG switch stability. You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -daglim <n>
- (AMD Polaris, Baffin, Tonga, or Fiji cards only) Limit the DAG size to <n> MB to allow mining on 4 GB cards a few weeks after epoch 373 on Windows (or 381 on Linux). The possible values except the exact DAG limit are also 0 (turn off the DAG limit), 1 (automatic DAG limit size, usually 4023 MB under Windows; this is the default). Note that the hashrate will drop significantly with each epoch after the DAG limit is in effect. If the hashrate drops too much (e.g. from 28 MH/s to just
2-3 MH/s, you need to use lower value, for example
-daglim 3996or even lower. - -dagrestart <n>
- Restart the miner when allocating buffer for a new DAG epoch. The possible values are: 0 - never, 1 - always, 2 - auto (the miner decides depending on the driver version). This is relevant for 4 GB AMD cards, which may have problems with new DAG epochs after epoch 350.
- -lidag <n>
- Slow down DAG generation to avoid crashes when switching DAG epochs (0-3, default: 0 - fastest, 3 - slowest). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -gser <n>
- Serializing DAG creation on multiple GPUs (0 - no serializing, all GPUs generate the DAG simultaneously, this is the default; 1 - partial overlap of DAG generation on each GPU; 2 - no overlap (each GPU waits until the previous one has finished generating the DAG); 3-10 - from 1 to 8 seconds delay after each GPU DAG generation before the next one)
- -gpureset <n>
- Fully reset GPU when paused (0 - no, 1 - yes; default: no, except on 1080Ti). You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -rvram <n>
- Minimum free VRAM in MB (-1: don’t check; default: 384 for Windows, and 128 for Linux)
- -altinit
- Use alternative way to initialize AMD cards to prevent startup crashes
- -wdog <n>
- Enable watchdog timer: 1 - yes, 0 - no (1 is the default). The watchdog timer checks periodically if any of the GPUs freezes and if it does, restarts the miner (see the
-rmodecommand-line parameter for the restart modes) - -wdtimeout <n>
- Watchdog timeout (30 - 300; default 45 seconds). You can use this parameter to increase the default watchdog timeout in case it restarts the miner needlessly
- -rmode <n>
- Selects the restart mode when a GPU crashes or freezes:
:0: disabled - miner will shut down instead of restarting
:1: restart with the same command line options - this is the default
:2: reboot (shut down miner and execute
reboot.bat) - -log <n>
- Selects the log file mode: :0: disabled - no log file will be written :1: write log file but don’t show debug messages on screen (default) :2: write log file and show debug messages on screen
- -logfile <name>
- Set the name of the logfile. If you place an asterisk (*) in the logfile name, it will be replaced by the current date/time to create a unique name every time PhoenixMiner is started. If there is no asterisk in the logfile name, the new log entries will be added to end of the same file. If you want to use the same logfile but the contents to be overwritten every time when you start the miner, put a dollar sign ($) character in the logfile name (e.g.
-logfile my_log.txt$). - -logdir <path>
- Set a path where the logfile(s) will be created
- -logsmaxsize <n>
- Maximum size of the logfiles in MB. The default is 200 MB (use 0 to turn off the limitation). On startup, if the logfiles are larger than the specified limit, the oldest are deleted. If you use a single logfile (by using
-logfile), then it is truncated if it is bigger than the limit and a new one is created. - -config <name>
- Load a file with configuration options that will be added to the command-line options. Note that the order is important.
For example, if we have a
config.txtfile that contains-cclock 1000and we specify command line-cclock 1100 -config config.txt, the options from theconfig.txtfile will take precedence and the resulting -cclock will be 1000. If the order is reversed (-config config.txt -cclock 1100) then the second option takes precedence and the resulting -cclock will be 1100. Note that only one-configoption is allowed. Also note that if you reload the config file withckey or with the remote interface, its options will take precedence over whatever you have specified in the command-line. - -timeout <n>
- Restart miner according to -rmode after n minutes
- -pauseat <hh:mm>
- Pause the miner at hh:mm (24 hours time). You can specify multiple times:
-pauseat 6:00,12:00 - -resumeat <hh:mm>
- Resume the miner at hh::mm (24 hours time). You can specify multiple times:
-resumeat 8:00,22:00 - -gswin <n>
- GPU stats time window (5-30 sec; default: 15; use 0 to revert to pre-2.8 way of showing momentary stats)
- -gsi <n>
- Speed stats interval (5-30 sec; default: 5; use 0 to disable). The detailed stats are still shown every 45 seconds and aren’t affected by the
-gsivalue - -astats <n>
- Show advanced stats from Web sources (0: no; 1: yes). By default the coin exchange rates are updated every 4 hours, and the coin difficulty is updated every 8 hours. You can increase these periods by specifying for example
-astats 12, which will increase update periods to 12 and 24 hours respectively - -gpow <n>
- Lower the GPU usage to n% of maximum (default: 100). If you already use
-mi 0(or other low value) use-liinstead. You may specify this option per-GPU. - -li <n>
- Another way to lower the GPU usage. Bigger n values mean less GPU utilization; the default is 0. You may specify this option per-GPU.
- -resetoc
- Reset the HW overclocking settings on startup
- -leaveoc
- Do not reset overclocking settings when closing the miner
Hardware control options (you may specify these options per-GPU)
- -hwm <n>
- Frequency of hardware monitoring (one setting for all cards, the default is 1): 0 - no HW monitoring or control, 1 - normal monitoring, 2 to 5 - less frequent monitoring.
- -tt <n>
- Set fan control target temperature (special values: 0 - no fan control, negative - fixed fan speed at n %)
- -hstats <n>
- Level of hardware monitoring: 0 - temperature and fan speed only; 1 - temperature, fan speed, and power; 2 - full (include core/memory clocks, voltages, P-states). The default is 1.
- -pidle <n>
- Idle power consumption of the rig in W. Will be added to the GPU power consumption when calculating the total power consumption of the rig.
- -ppf <n>
- The power usage of each GPU will be multiplied by this value to get the actual usage. This value is in percent, so for example if the GPU reports 100 W power usage and you have specified -ppf 106 the GPU power usage will be calculated to be 100 * (106 / 100) = 106 W. This allows you to correct for the efficiency of the PSUs and the individual GPUs. You can also specify this value for each GPU separately.
- -prate <n>
- Price of the electricity in USD per kWh (e.g.
-prate 0.1). If specified the miner will calculate the rig daily electricity cost - -fanmin <n>
- Set fan control min speed in % (-1 for default)
- -fanmax <n>
- Set fan control max speed in % (-1 for default)
- -fcm <n>
- Set fan control mode (0 - auto, 1 - use VBIOS fan control, 2 - forced fan control; default: 0)
- -fanidle <n>
- (Linux only) Set idle fan speed in % (-1 is auto, the default is 20)
- -fpwm <n>
- (Linux only) Fan PWM mode (0 - auto, 1 - direct, 2 - Polaris, 3 - Vega, 4 - Radeon VII, Navi; default: 0)
- -tmax <n>
- Set fan control max temperature (0 for default). If this feature is not supported by the driver,
-ttliis set to the same temperature instead - -powlim <n>
- Set GPU power limit in % (from -75 to 75, 0 for default)
- -cclock <n>
- Set GPU core clock in MHz (0 for default). For Nvidia cards use relative values (e.g. -300 or +400)
- -cvddc <n>
- Set GPU core voltage in mV (0 for default)
- -mclock <n>
- Set GPU memory clock in MHz (0 for default). For Nvidia cards use relative values (e.g. -300 or +400)
- -mvddc <n>
- Set GPU memory voltage in mV (0 for default)
- -tstop <n>
- Pause a GPU when temp is >= n deg C (0 for default; i.e. off)
- -tstart <n>
- Resume a GPU when temp is <= n deg C (0 for default; i.e. off)
- -mt <n>
- VRAM timings (AMD under Windows only): 0 - default VBIOS values; 1 - faster timings; 2 - fastest timings. The default is 0. This is useful for mining with AMD cards without modding the VBIOS.
- -leavemt
- Do not reset memory timing level (
-mt) to 0 when closing - -ttli <n>
- Lower GPU usage when GPU temperature is above n deg C. The default value is 0, which means do not lower the usage regardless of the GPU temperature. This option is useful whenever -tmax is not working. If you are using both
-ttand-ttlioptions, the temperature in-ttshould be lower than the-ttlito avoid throttling the GPUs without using the fans to properly cool them first. - -straps <n>
- Memory strap level (Nvidia cards 10x0 series only). The possible values are 0 to 6. 0 is the default value and uses the default timings from the VBIOS. Each strap level corresponds to a predefined combination of memory timings (
-vmt1,-vmt2,-vmt3,-vmr). Strap level 3 is the fastest predefined level and may not work on most cards, 1 is the slowest (but still faster than the default timings). Strap levels 4 to 6 are the same as 1 to 3 but with less aggressive refresh rates (i.e. lower-vmrvalues). - -straps <n>
- Memory strap level (AMD Vega cards only). The possible values are 0 to 5. 0 is the default value and uses the default timings from the VBIOS. Each strap level corresponds to a predefined combination of memory timings. Strap level 5 is
the fastest level and may not work on most cards, 1 is the slowest (but still faster than the default timings). Note that straps for AMD cards are experimental and may lead to crashes or instability.
-vmt1,-vmt2, and-vmt3parameters have no effect on AMD cards - -vmt1 <n>
- Memory timing parameter 1 (0 to 100, default 0)
- -vmt2 <n>
- Memory timing parameter 2 (0 to 100, default 0)
- -vmt3 <n>
- Memory timing parameter 3 (0 to 100, default 0)
- -vmr <n>
- Memory refresh rate (0 to 100, default 0). For AMD cards you may also use
-rxboost - -nvmem <n>
- Force using straps on unsupported Nvidia GPUs (0 - do not force, 1 - GDDR5, 2 - GDDR5X). Make sure that the parameter matches your GPU memory type. You can try this if your card is Pascal-based but when you try to use
-strapsor any other memory timing option, the card is shown as “unsupported”. - -rxboost <n>
- Memory refresh rate on AMD cards (0 - default value, 1 - predefined value that should work on most cards, 2 to 100 - increasingly aggressive settings). If you want to fine tune the value, you may run
the miner with
-rxboost 1, write down the corresponding-vmrvalues that are showed in the log file, and then use-vmrinstead with adjusted values. - -vmdag <n>
- Reset straps to default during DAG generation (default: 1)
- -mcdag <n>
- Reset GPU memory clock to default during DAG generation. Nvidia only, default: 0 (turned off).
This may allow you to set higher memory overclock on your Nvidia cards without risking corrupt
DAG buffer, which can lead to excessive number of stale shares.
Under Linux this option will execute the
daggen.shscript (if present in the current directory) for each GPU, passing the GPU index as the first argument, and PCIE bus ID as second argument. The miner will then wait for about 7 seconds before starting DAG generation to allow the script enough time to reset the memory overclock.
General Options
- -list
- List the detected GPUs devices and exit
- -v,–version
- Show the version and exit
- -vs
- Show short version string (e.g.
4.1c) and exit - -h,–help
- Show information about the command-line options and exit
Per-GPU options
Some of the PhoenixMiner options can provide either the same setting for all GPUs, or a different
setting for each of the GPUs. For example, to specify the -gt value for all cards you would write
-gt 90 but if you want to specify a different GT value for each of the cards, use something like this:
-gt 20,15,40,90,90 for a five-GPU mining rig. This would set GT to 20 for the first GPU, 15 for the second
GPU, and so on. If you specify less values than you have GPUs, the rest of the GPUs will use the default
value for the parameter.
You can also use another, more flexible way of specifying different values for the different cards.
This is best explained by example: -cclock *:1100,1-3:1090,4:1300 - here we are setting core clock
to 1100 MHz for all cards, except the cards 1 to 3, on which it is set to 1090 MHz, and card 4 to 1300 MHz.
The part before the colon (:) is the selector, which selects the GPUs for which the value after the colon is applied. The selector can be:
- single GPU index: e.g.
5:1000sets 1000 for the 5th GPU - range of GPU indexes: e.g
2-5:1200sets 1200 for the GPUs 2,3,4, and 5 - asterisk, which sets the value for all GPUs
- label
amdornvidia: e.g.amd:1090sets the value to 1090 for all AMD cards - arbitrary string that starts with letter and can contain letters, numbers and asterisks,
which is matched with the GPU name as listed by PhoenixMiner. Example:
gtx*1070:+500will set value +500 for all cards which contain ‘gtx’ and ‘1070’ in their names with anything between them. This will match ‘Nvidia GeForce GTX 1070’ but not ‘Nvidia GeForce 1070’.
Note that if more than one selector matches given card, than only the last one counts.
Example: -cclock *:1100,1-4:1090,2:1300 will set card 2 to 1300; cards 1,3, and 4 to 1090;
and the rest of the cards to 1100 MHz core clock.
